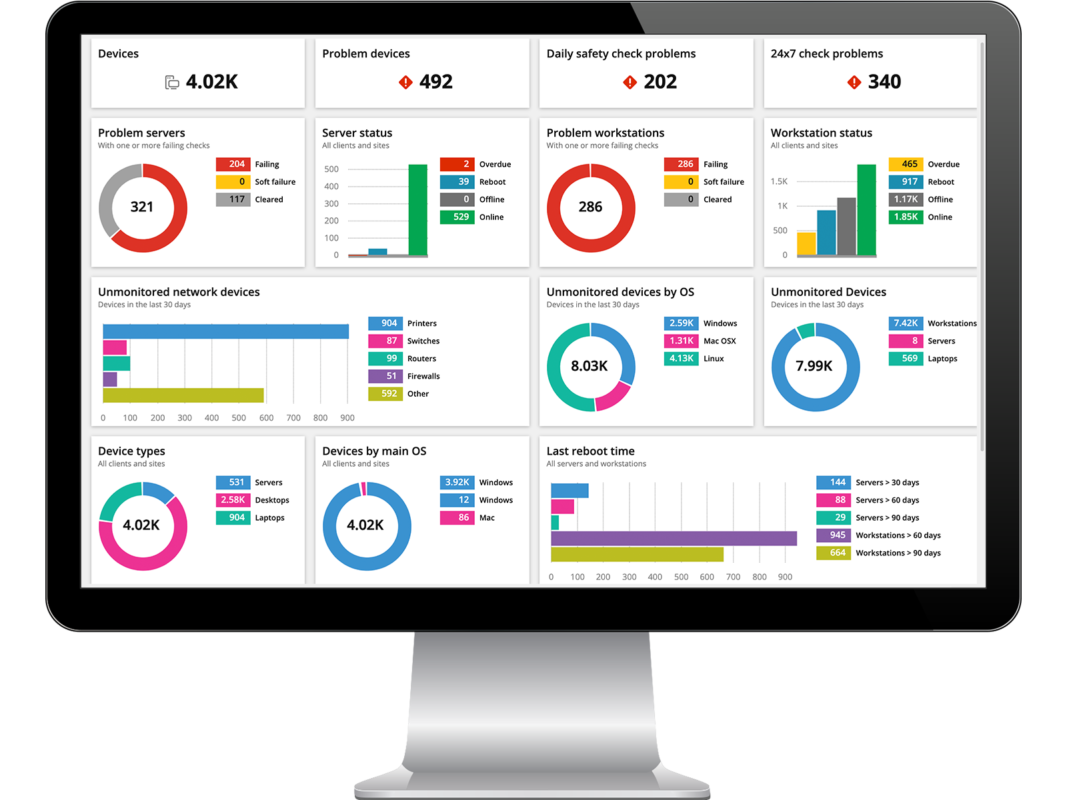
Infrastructure monitoring is crucial to successfully operating any business, platform, or service. Infrastructure monitoring tools allow users to figuratively keep two fingers on their infrastructure's pulse. Real-time monitoring is a technique that will enable you to determine the current state of servers and network devices. IT infrastructure monitoring tools allow organizations to identify and resolve IT infrastructure problems before they can adversely affect critical business processes. This enables I&O leaders to monitor and collate physical and virtual entities' availability and resource utilization metrics, including servers, containers, network devices, database instances, raid, hypervisors, and storage.
In addition to monitoring the entire infrastructure and business processes, they can help plan upgrades before outdated systems cause failures and respond to issues as soon as problems become evident. They can also help ensure that any necessary outages have minimal user impact. These days, there is a heavy emphasis placed on users' ability to stay connected. So how can you ensure that users can enjoy countless digital experiences seamlessly? The answer to such an important question lies in infrastructure monitoring. Imagine the day there's a sudden spike in traffic on your server which causes issues for users trying to connect. If you had been using infrastructure monitoring tools, you could have been alerted to the increased traffic. This could have given you time to set up another server and avoid overutilizing the current server. Or if the server overutilization was due to the cyber attack, IT Team can act on time to save the organization from damage. This is a perfect example of how infrastructure monitoring proves invaluable.
SOC Team detects, prioritizes, investigates, and responds to security threats. It combines threat intelligence, machine learning-based anomaly detection, and rule-based attack detection techniques to detect sophisticated attacks, and incidents are managed effectively and remediating detected threats. Security Operations Centers (SOCs) use various tools to monitor and protect an organization’s networks and systems from cyber threats. Some of the most common tools used in SOCs include: Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) — monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity and can automate actions to block or quarantine suspected threats. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems — SIEMs collect and analyze log data from various sources, such as network devices, servers, and applications, to identify potential security threats and suspicious activity. Threat Intelligence Platforms — These platforms gather and analyze intelligence from various sources, such as threat feeds and open-source information, to identify known and emerging threats. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools — These tools monitor endpoint activities, such as process execution and file access, in order to detect and respond to advanced threats. Vulnerability Management Platforms — These platforms scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities and help organizations prioritize and remediate them. Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) Tools — These tools provide real-time visibility into network traffic, such as session details, protocols, and network behaviors, to detect and respond to threats. Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools — These tools are used to secure and manage user access to network resources, applications, and data and to monitor and report on user activities. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) tools —These tools are increasingly used to automate threat detection, analysis, and response.
When external service providers effectively deliver IT-enabled business processes, application services, and infrastructure solutions for business outcomes. Because today's IT is exceptionally dynamic and volatile, building in-house capacity is not cost-effective anymore due to the need of diverse skillsets. Whereas managed IT companies invest in talent and subject matter experts. Services include methods to protect organizations against Ransomware, DDoS, phishing, and other security threats, as well as add business continuity model by protecting data backups because computer attack patterns shift and threats to networks change and grow almost daily, it is critical that organizations achieve reliable information security. Investment decisions about information security are best considered in the context of managing business risk. Risks can be accepted, mitigated, avoided, or transferred. Outsourcing selected managed security services (MSS) by forming a partnership with a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) is often a good solution for transferring information security responsibility and operations. Although the organization still owns information security risk and business risk, contracting with an MSSP allows it to share risk management and mitigation approaches.
In the background of numerous cyber-attacks being launched globally by cyber criminals. Each business today needs to keep itself ready for the worst disaster, be it from nature or man-made. Business needs to be able to recover quickly from any event that stops day-to-day operations, no matter what industry or size. With a disaster recovery exercise, a company can experience data loss, reduced productivity, out-of-budget expenses, and reputational damage that can lead to lost customers and revenue. Technology plays an increasingly important role in every aspect of business, with applications and services enabling companies to be more agile, available, and connected. A disaster recovery plan aims to reduce damage or disruption and recover as quickly as possible in the event of a disaster that leads to system failure. DR plans usually have two key components: a recovery time objective (RTO) and a recovery point objective (RPO).
The RTO is the time it takes to recover systems after an outage, which determines how much time you need to restore business operations. The RPO reveals how often a backup needs to take place by setting a limit for the length of time the company can sustain data loss. Creating a DR plan can also have immediate benefits. For instance, because developing the plan involves conducting an audit of your IT assets and Service Level Agreements, you’ll better understand the organization’s IT estate. A comprehensive disaster recovery strategy should include detailed emergency response requirements, backup operations, and recovery procedures. DR strategies and plans often help form a broader business continuity strategy, which includes contingency plans to mitigate impact beyond IT infrastructure and systems, allowing all business areas to resume normal operations as soon as possible. GuardianTech is a promising Managed It Provider to help.
Cyber threat hunting is a proactive cyber defense activity. Threat hunting is essential for any successful business because sophisticated threats can pass automated cybersecurity. Although automated security tools and tier 1 and 2 security operations center (SOC) analysts should be able to deal with roughly 80% of threats, you still need to worry about the remaining 20%. The remaining 20% of threats are more likely to include sophisticated threats that can cause significant damage. More than ever, we need automation to move security from human to machine speed and new security strategies such as proactive threat hunting.
Companies can fall to the ground overnight because of a sudden data loss. Therefore, security service providers can’t afford to believe that their security system is impenetrable. They always remain vigilant for the next threat or vulnerability. Rather than sit back and wait for threats to strike, cyber threat hunting develops hypotheses based on knowing the behaviors of threat actors and validating those hypotheses through active searches in the environment. With threat hunting, our experts don’t start from an alert or even an indicator of compromise (IOC) but from deeper reasoning and forensics. Cyber-threat hunting aggressively assumes that a breach in the enterprise has or will occur. Security personnel hunt down threats in their environment rather than deploy the latest tool. Managed service providers have several tools, security professionals, and subject-matter experts to deal with threats.
Red and blue teams play an important role in defending against advanced cyber-attacks that threaten business communications, sensitive client data, or trade secrets. Red teams are offensive security professionals who are experts in attacking systems and breaking into defenses. Blue teams are defensive security professionals responsible for maintaining internal network defenses against all cyber-attacks and threats. Red teams simulate attacks against blue teams to test the effectiveness of the network’s security. Red teams often consist of independent ethical hackers who evaluate system security in an objective manner. Blue teams perform risk assessments by identifying threats against each asset and the weaknesses these threats can exploit. By evaluating the risks and prioritizing it, the blue team develops an action plan to implement controls that can lower the impact or likelihood of threats materializing against assets. Standard penetration scans are for Active Directory penetration, network and gateway firewall penetration, web application penetration (on financial transaction websites such as banks), phone application penetration, ATM penetration, and website penetration to identify vulnerabilities.
Data center management is the discipline of planning and operating data center facilities and the IT infrastructure within them to maximize uptime, reduce overhead costs, optimize IT resources, and ultimately honor service level agreements (SLAs) from the service provider. Data center management will also encompass other aspects of the facility, such as human resources, capacity planning, business services management, Data Security, and Cyber Security but not limited to these services.
GuardianTech use reliable technologies and strategies developed over the years to help us manage data center for customers with more granular insights and control over every aspect of data center operation. This can range from performance to monitoring server racks, including performing backups, cyber security protection, performing administrative activities on IT equipment remotely, but not limited to.
However, despite progress in formalizing data center operations, each is wholly unique, requiring its own brand of planning and monitoring to achieve visibility and control over its systems. To that end, GuardianTech uses Data center infrastructure management (DCIM) software that provides a powerful; Our intelligent advanced DCIM solution incorporates the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, along with automation, to monitor and respond to data center problems effectively. GuardianTech use various other world-class technology to manage the data center of their customer. That’s our expertise, and that’s what we do.
Cloud Infrastructure Management is a rapidly evolving field focused on providing businesses of all sizes with reliable and optimized services and effectively managing their computing resources. It involves managing physical, virtual, and cloud infrastructures and leveraging advanced software and technologies such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Cloud Infrastructure Management maintains oversight and administrative control of cloud computing products and services and how users access control, data, applications, and services, whether the deployment is in public, private, or hybrid cloud environments.
Cloud infrastructure management is the discipline and technology support, backed by technology tools and service providers, that brings appropriate oversight to cloud usage. It enables businesses to create, configure, scale, and retire cloud infrastructure as needed. Cloud infrastructure management is like a command center or central nervous system for cloud environments. Cloud infrastructure management maximizes operational flexibility and agility while maintaining cost efficiencies, providing the capabilities to manage consolidated computer resources securely. Cloud infrastructure management ultimately makes the potential of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies both attainable and sustainable. Managing cloud infrastructure comes with an adviseable design and management strategy that experts should handle.
Ensuring that cybersecurity protections are sustained is essential. The first part of the cyber security risk management process is a cyber risk assessment or risk analysis. A cybersecurity risk assessment is an assessment of an organization’s ability to protect its information and information systems from cyber threats. The purpose of a cybersecurity risk assessment is to identify, assess, and prioritize risks to information and information systems. It also helps organizations communicate their risks to stakeholders and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources to reduce those risks. A cybersecurity risk analyses is a process that helps organizations determine key business objectives and then identify the appropriate IT assets and their objectives. It involves the identification of cyber-attacks that may negatively impact these IT assets. Risk analysis involves identifying the various information assets that could be affected by a cyber-attack (such as hardware, servers, laptops, switches, routers, customer data, intellectual property, etc.
An IT Security Audit’s sole purpose is for a third-party to verify whether an organization is operating according to legal standards and guidelines. The security audit measures an organization’s current reality and benchmarks it against a specific industry standard, Data backup strategies, IT security strategies and best practices. Whereas a Vulnerability Assessment is a high-level, proactive evaluation of an organization’s cybersecurity before an official IT Audit. It provides an overview of an organization’s cybersecurity landscape, providing an opportunity to identify where security policies, practices, and procedures are robust and meet best practices as well as identify gaps and vulnerabilities. A typical security audit will review.